Emotion AI interviews
Analyzing performance and reactions to EAI in mock job interviews,
The University of Texas at Austin (2023)
SITUATION
Our research team wanted to evaluate the impact of AI facial emotion recognition on people in remote job interviews.
Background
AI’s challenges with transparency and explainability have become ingrained through all stages of the hiring process in the last decade. Job applicants who don't fit the benchmark data may experience encoded bias at scale and companies may lose out on candidates, reducing diversity in the workplace.
Goal
In this pilot study, we designed a mock interview experiment to examine the impact of AI-driven facial emotion recognition on interviewees.
Research Questions
-
How does emotion-tracking/EAI make participants feel?
-
What information do participants want to see in their EAI results?
-
What is the best visualization of emotion-tracking reports?
Desired Outcomes
-
Job Applicants: Promote emotion-tracking AI tools to enhance self-awareness, improve video interview performance, and potentially challenge biased systems.
-
Hiring Companies: Support the adoption of AI tools to increase transparency, reduce unconscious bias, and promote diversity in hiring.
-
AI Tool Creators: Advocate for the use of diverse datasets in AI facial analysis tools to ensure fairness and accuracy for a broad user base.
TASK
I led UX research, design, and project management
Team
-
1 UX researcher/designer and project manager (me, MS student)
-
1 AI technology researcher and app developer (MS student)
-
1 data scientist and app developer (MS student)
-
1 literature researcher for critical analysis (PhD student)
What I Did
Developed research methods, managed the project timeline and defined deliverables, conducted interviews, designed customized interactive reports for each participant and project presentations
Timeline
Jan - April 2023 (3 months)
Tools
Figma, Google Survey, Google Docs, Google Sheets, Zoom
Skills
UX, prototyping, survey design and analysis, remote interviews, remote interviews, project management, presentation design, academic writing, and IRB human subjects research training
ACTION 1
I recommended IRB training and designed a survey for recruitment. We conducted 9 remote 1:1 mock interviews and follow-ups, revealing reactions and attitudes towards the EAI analysis.
Human Subjects Research Training
IRB training helped us identify risks to participants.
Recruitment
-
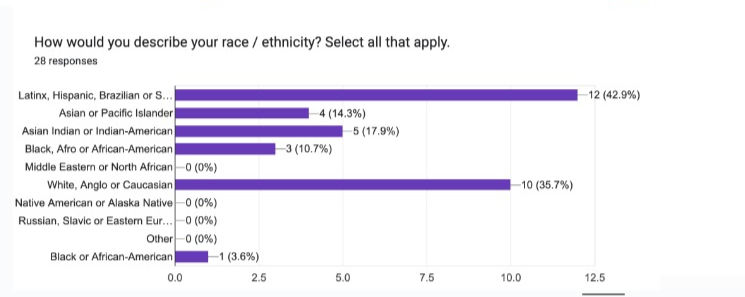
A screener survey with 12 questions was designed to obtain a relevant and equitable sampling to meet our participant quota (from which we collected 27 viable respondants).
-
Data cleaning and prioritization of demographics resulted in 12 shortlisted participants with 4 alternates.
-
1 participant backed out
-
2 were non responsive
-
Leaving us with 9 participants we could interview via Zoom over 1 week
-
Recorded Mock Interviews
-
We obtained verbal informed consent to record at the start of our sessions
-
We followed a script asking 3 behavioral questions.
-
We asked 3 post-interview questions to learn more about participants' perception of their interview experience.
ACTION 2
We asked 3 questions designed to elicit a neutral response, stressed response, and confident response. We attempted to create similar conditions for each participant.
EAI Sentiment Analysis
-
We used an open source Python library for sentiment analysis of videos
-
Multi Cascade Convolutional Neural Network (MTCNN) model
-
Dataset - FER 2013, Pierre Luc Carrier and Aaron Courville, ICML: Challenges in Representation Learning
-
-
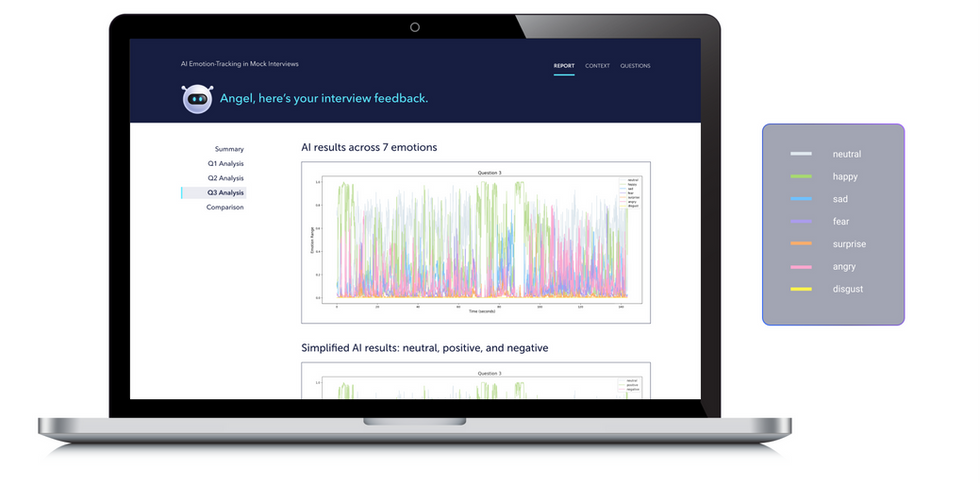
It analyzed videos per frame for 7 emotions
-
Neutral, Happy, Sad, Fear, Surprise, Anger, Disgust
-
Data Processing
-
We analyzed the output data in CSV format with timestamps and emotion analysis output
-
We combined the model's output data with information from screener survey
-
We generated insights by looking at how each participant's emotion may differ when analyzing emotions for each question and demographic comparison
Participant's permission was obtained to share this video clip.
ACTION 3
I prototyped an interactive report for each participant, enabling them to compare the video clips of their responses to the EAI data visualizations and comparative data.
Mixed reactions to AI emotion analysis
-
6/9 participants agreed with the EAI analysis results in hindsight, even if initially surprised
-
2 participants were ambivalent
-
1 participant had a negative sentiment
Participant Suggestions for Improvement of AI Tool
-
Detection of stuttering and overuse of filler words
-
Providing comparisons to human expert evaluations
-
Chatbot integration to practice interview questions
-
Enable holistic evaluation, not just by facial expression
Design insights
-
Provide a timebar on video playback and AI analysis chart so user can see the correlation
-
Users would like to connect data performance to behavioral insights and suggestions for improvement
-
Practicing with a real person via zoom vs. practicing alone with an AI interface may yield different results
-
Benchmarking performance against other users interested participants but also caused some discomfort
RESULTS
There are concerns about fairness, bias, candidate well-being and the need for transparency in AI usage
Shift in Perception
-
4 participants reported a positive change in feelings after seeing results
-
3 participants had no change in feelings
-
1 participant became more concerned about AI in general
Openness to Using AI Tools for Interview Prep
-
7 participants would consider using AI tools for mock interview preparation
-
2 participants would not consider using such a tool
-
Some see it as a useful way to "gamify" the process and adjust their performance.
Awareness and Concerns
-
The study raised awareness about the use of AI in interviews, especially if it makes the final hiring decision.
-
Revealed concerns about AI bias, the potential for "fakeness" in hiring, and the need for human elements in the interview process.
Results Summary
Results indicate a societal opennes to AI in hiring but highlights concerns about fairness, bias, candidate well-being, and the need for transparency in AI usage that businesses must address for ethical implementation.

"I'd rather start my own business than use AI to become someone I'm not."
Participant 3
RELEVANCE
For businesses, these findings are crucial for designing ethical and transparent AI tools that...
-
Enhance talent acquisition
-
Manage reputational risks
-
Balance efficiency with a positive candidate experience
EVOLUTION
Next time, I would maintain rigor, but stay nimble.
Process Insights
-
By beginning with a detailed research plan, I was able to streamline process, keep the team aligned, and deliver on goals.
-
Align on goals and protocols so everyone is rowing in the same direction and findings are defensible.
-
Reality will force plans to shift, so stay nimble, have some backup plans, and discuss as a team how this impacts the study.
-
Meet people where they're at to enable fruitful discussions, both within the team and with research participants.
-
It is difficult to mimic a realistic interview experience for the collection of accurate data when participants are aware it is not a real interview.
Future work can address the mismatch between how ML algorithms work and the realities of interviewing as a person with "disability."
Building on these findings, the next step is to push AI hiring practices toward greater equity, accessibility, and inclusion for people with disabilities.
Future Work
-
Design AI hiring tools that treat disability as diversity, not outliers.
-
Bring disabled voices to the table in shaping systems and regulations.
-
Push for better policies that address disability and age bias, not just gender and race.
-
Create fairer training data that better reflects real-world diversity.
-
Show how inclusive hiring AI builds stronger, more innovative workforces.